Stroke Outcomes and Results at Novant Health
Giving you the highest quality care is our first priority.
At Novant Health we support the nationwide effort to ensure that patients coming into the hospital with specific conditions receive recommended care based on medical research and consensus of opinion of physician experts.
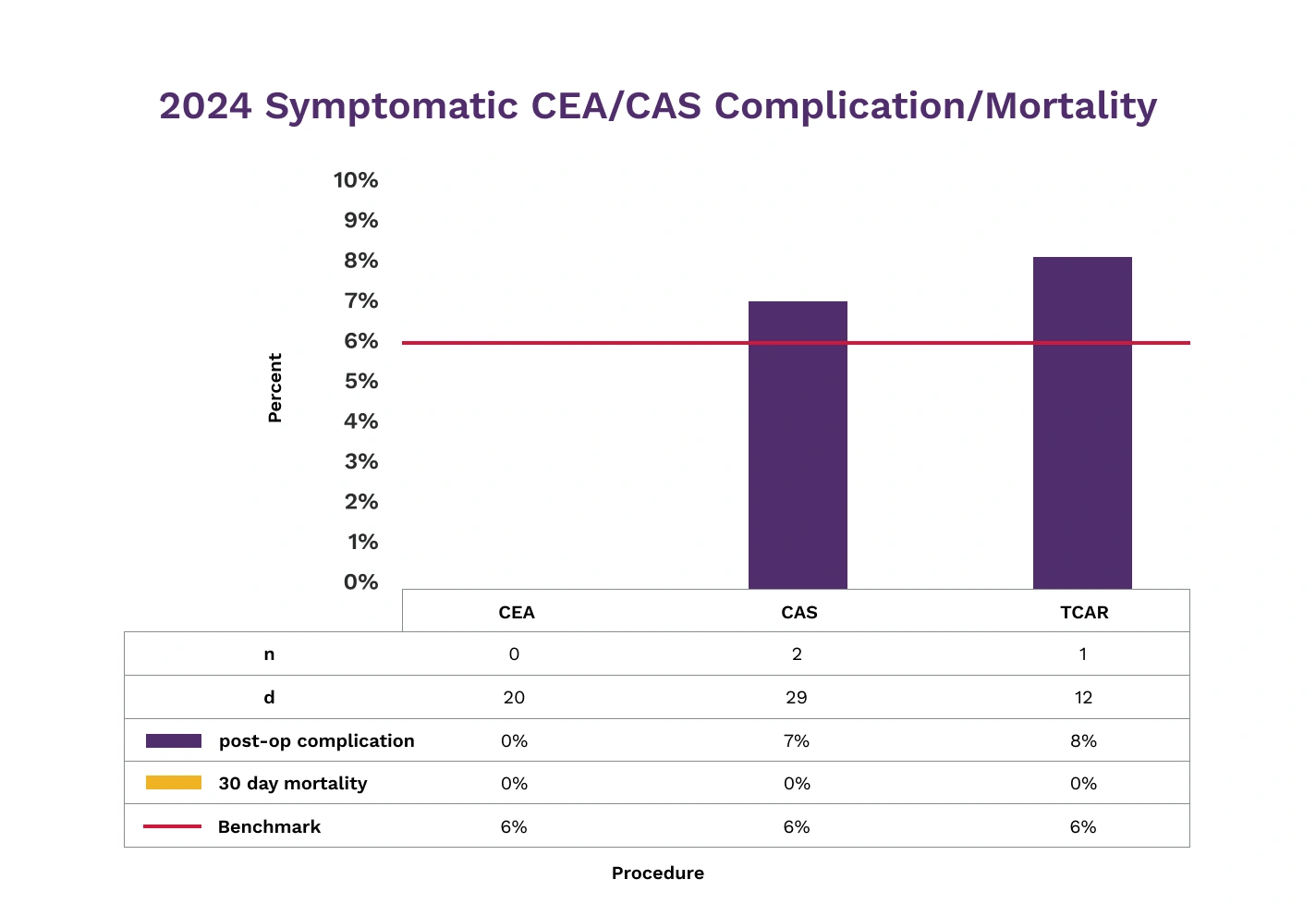
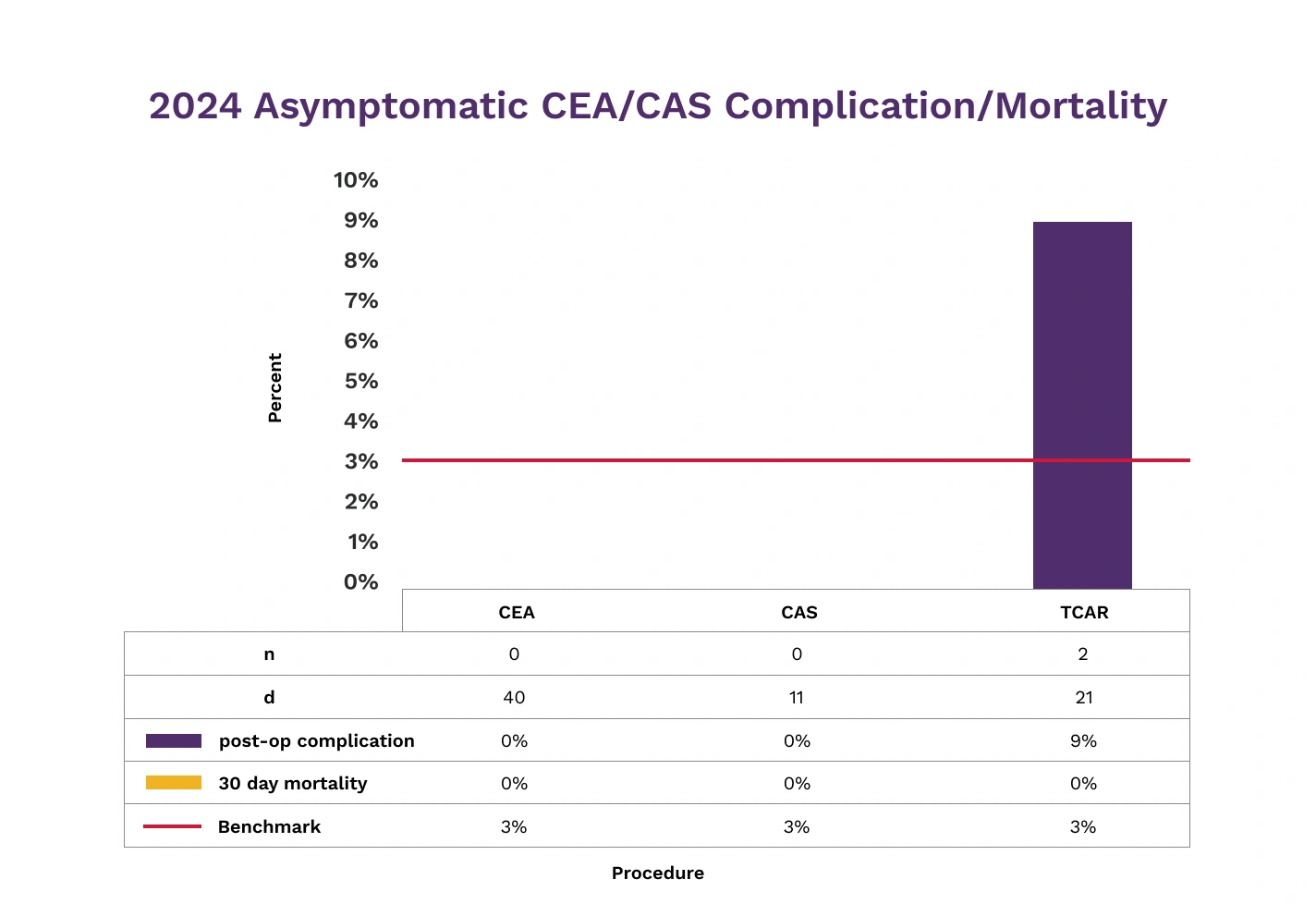
When available, Novant Health facilities use nationally established benchmarks for comparison of outcomes at our facilities. We are providing the following information about two procedures performed at Forsyth Medical Center and Presbyterian Medical Center: carotid artery stenting and aneurysm coiling as well as complications associated with these procedures.
A quality measure is medical information from patient recorded converted into a rate of percentage that shows how well hospitals care for their patients. We encourage you to discuss the benefits and risks of these procedures with your physician.
Forsyth Medical Center
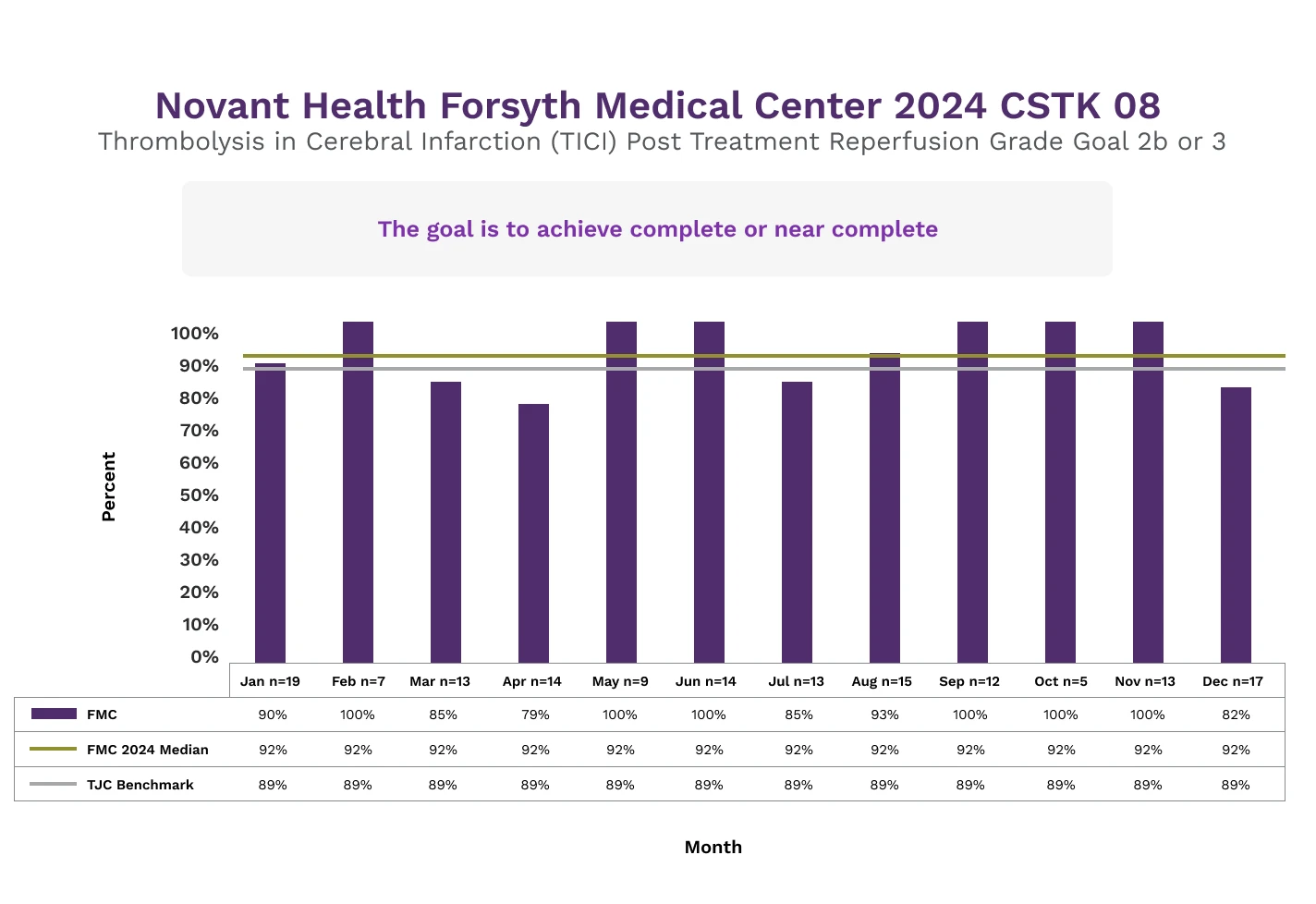
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a catheter to remove a blood clot from the brain after an ischemic stroke. After making a small incision in the groin, doctors’ thread a thin tube through the blood vessels to the clot. It has become the standard of care for removing blood clots in the brain. The thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) grading system is a tool for determining the response of this type of therapy to evaluate the degree of restored blood flow to the brain MT. A grade of 2b indicates complete filling of the expected vascular territory, but with a perceptibly slower filling rate than normal.
Presbyterian Medical Center
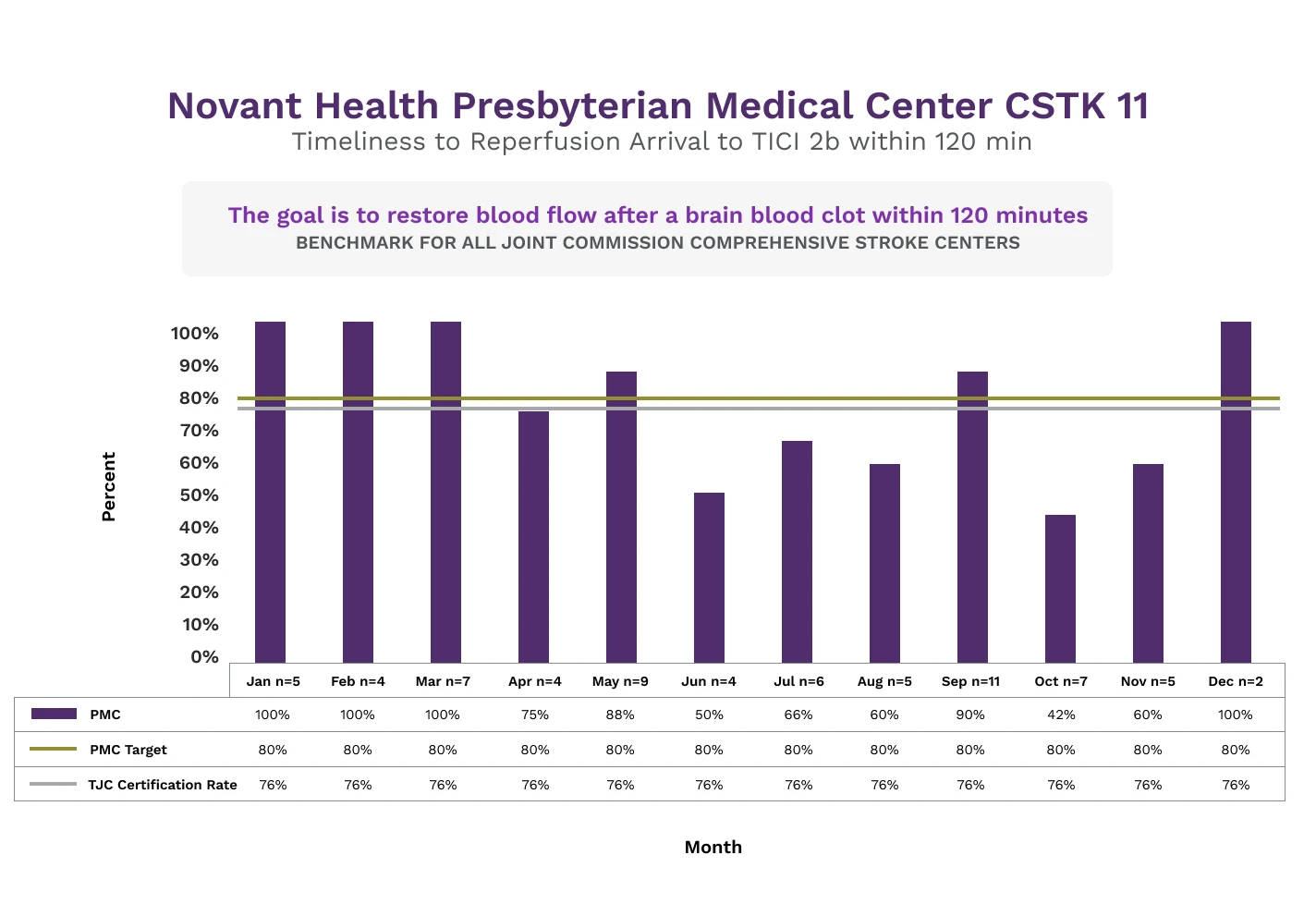
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a catheter to remove a blood clot from the brain after an ischemic stroke. After making a small incision in the groin, doctors’ thread a thin tube through the blood vessels to the clot. It has become the standard of care for removing blood clots in the brain. The thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) grading system is a tool for determining the response of this type of therapy to evaluate the degree of restored blood flow to the brain MT. A grade of 2b indicates complete filling of the expected vascular territory, but with a perceptibly slower filling rate than normal.